In these hydrocarbons one or more of the hydrogen atom s is replaced by a halogen group 17. And also if it is allylic or benzylic.

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKYL HALIDES a Boiling point.

. The halogen atom is attached to a sp 2 hybridized carbon atom in aryl halides. They are denser than water and form a separate lower layer. 12 text -difluoro-3-iodocyclohexane text d.
9 Lessons in Chapter 29. Until the late 1980s alkyl halides called chloro-. Name and draw alkyl halides a.
They can also be manufactured from any organic precursors such as alkanes alkenes or alcohols and carboxylic acids. Alkyl Aryl Halides. 1122 text.
This is an unsaturated structure due to the presence of double bonds in the aromatic ring. In this lesson we will learn about alkyl halides and common. The below chart shows the boiling point of some simple haloalkanes.
Watch More Solved Questions in Chapter 22. If the compound is an alkyl halide indicate whether it is 1 2 or 3. Give IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides.
Identify the nucleophile substrate and leaving group in the general equations for reactions 1 and 2. B Aryl halides These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to the sp2-hybridised carbon atom of an aromatic ring. 13 text -dibromobenzene text e.
Alkyl halides have a linear or branched structure most of the times. An alkyl halide can be made by starting with an alkene and adding H-X to it. BPK 400 Room 300 temperature 200 100 0 CH 3 X CH 32 CH X CH 322 CH CH X Gas Gas Chlorides Bromides Iodides Figure 121.
Write the name and draw the structure of the alkyl group that corresponds to 0202. On the other hand aryl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms bonded covalently to benzene rings or aromatic groups. An aryl halide is a molecule having a halogen atom attached to an sp2 hybridized carbon in an aromatic ring directly.
Plan and predict the outcomes of the following chemi-cal reactons. Recognize alkyl halides as compared to vinyl and aryl halides c. The carbon-halogen bond is stronger than that of alkyl halides due to the presence of ring electrons.
A compound containing a halogen atom covalently bonded to an sp3 hybridized carbon atom given the symbol R-X Vinylic and Aryl Halides. The carbon-halide bond of alkyl halides has a low density of electrons compared to aryl halides. Reactivities of Alkyl Halides in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Before You Begin.
Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution S N2 b. Describe and compare the structures of alkyl halides and aryl halides. Draw structures for the following molecules.
Structural formula for an aryl halide is created by first drawing the aromatic structure and then replacing its hydrogen atoms with the halogen atoms specified as shown in Figure 223a. Recognize C α and C β in an alkyl halide 2. An alkyl halide A on reaction with magnesium in dry ether followed by treatment with ethanol gave 2-.
Consequently this functional group is polarized so that the carbon is electrophilic and the halogen is nucleophilic as shown. Recognize primary 1 o secondary 2 o and ter-tiary 3 o halides b. These dipole-dipole attractions must be very unimportant relative to the dispersion forces because the most polar molecule the chlorobenzene has the lowest boiling point of the three.
Circle any organic halide below that can undergo a S N1 or S N2 type substitution reaction. Aryl halides are always ringed structures. FIGURE CANNOT COPY.
Draw the structures of the following alkyl halides. Generally alkyl halides contain hydrogen atoms attached to the sp. The formation of less stable carbonium ion 2.
2-Name the halogen replace to halide that bonded to the alkyl group. Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question. Video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 22 Substituted Hydrocarbons and Their Reactions Glencoe Chemistry by Numerade.
Alkyl halide or haloalkanes are formed by the replacement of hydrogen atoms in an aliphatic hydrocarbon by halogen atoms Fluorine chlorine bromine or iodine. Well review your answers and create a Test Prep Plan for you based on. MAINIDEA Compare and contrast alkyl halides and aryl halides.
Classify each halo compound shown below as an alkyl vinyl or aryl halide. Alkyl Aryl Halides Chapter Exam Take this practice test to check your existing knowledge of the course material. To give a common name.
Draw structures for these alkyl and aryl halides. Chlorobenzene text b. If the halogen is bonded to an sp2 hybridized carbon it is a called a vinylic halide if it is bonded to a benzene ring it is called an aryl halide given the symbol Ar-X.
Boiling points of haloalkanes Notice that three of these have bps below room temperature taken as. Which of these has weakest C CI bond. 1 text -bromo-4-chlorohexane text c.
The aryl halides are insoluble in water. Alkyl halides and aryl halides are the two different types of substituted hydrocarbons compounds composed of hydrogen and carbon. Cl Cl 1-chloro-2-methylpropane 2R 3R 6S- 2 chloro 8 ethyl 36 dimethyl decane Cl Br Cl I F Br I Br F.
With the exception of iodine these halogens have electronegativities significantly greater than carbon. Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions as compared to alkyl halides due to 1. 1-Name all the carbon atoms for longest chain of the molecule as a separate alkyl group by replacing ane of alkane by yl.
Draw the structures of all substrates you will be using in this reaction and classify them as 1º 2º 3º aryl benzylic or some combina tion of these such as 1º benzylic. Longer carbon-halogen bond 4. Aryl halides also show dipole-dipole interactions.
The functional group of alkyl halides is a carbon-halogen bond the common halogens being fluorine chlorine bromine and iodine. Mathrmsp2 hybridized carbon attached to halogen a 123 b 245 c 25 d 45. The common names of alkyl halides are derived by naming the alkyl group followed by the halide.
Alkyl halides are organic compounds with the general formula RX where R denotes the alkyl group and X denotes the halogen. Connection to Earth Science Alkyl halides are widely used as refrigerants. Combine the names of the alkyl group and halide separating the words with a space.
The inductive effect 5. Alkyl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms covalently attached to aliphatic carbon atoms or carbon atoms in a straight hydrocarbon orientation. Name these alkyl groups.
Name the type of organic compound each substance. Define functional group and name the group present in each of the following structures. The carbon atoms here are in a cyclic orientation.
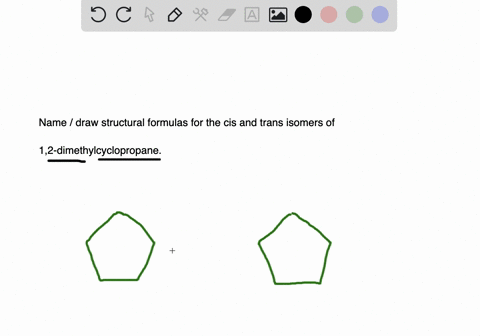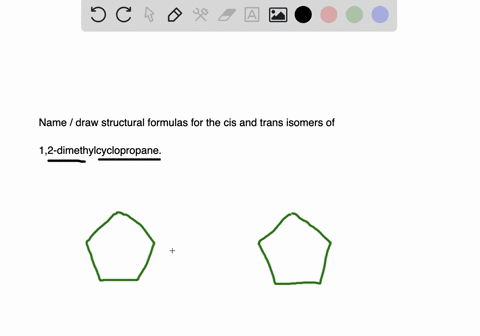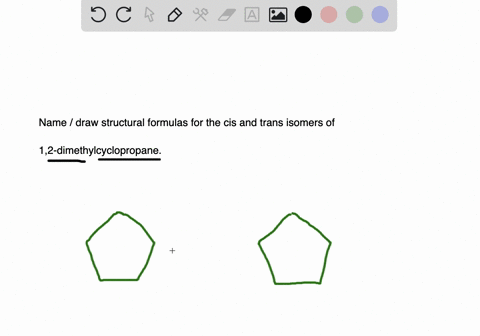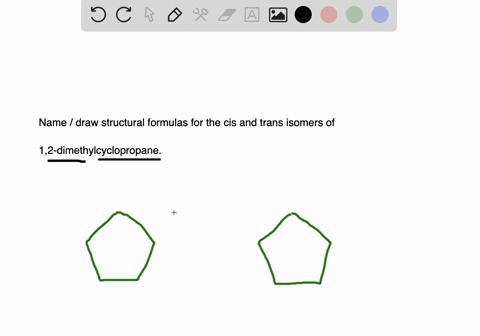
Name and write the structures of. The blank lines coming off of the carbons can be either another carbon or a hydrogen but since they are not important. Having learnt the classification of halogenated compounds let us now learn how these are named.
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
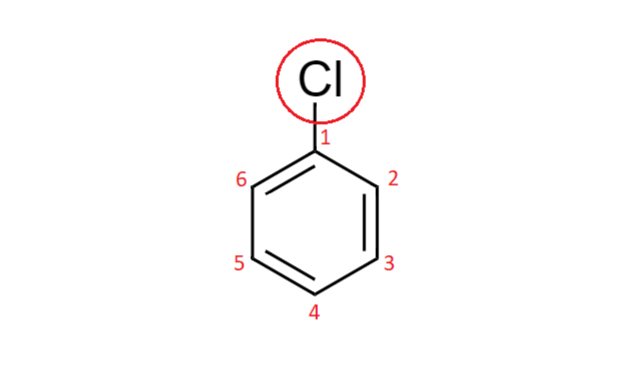
Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides A Chlorob Quizlet

Solved Xex Dx 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Chegg Com
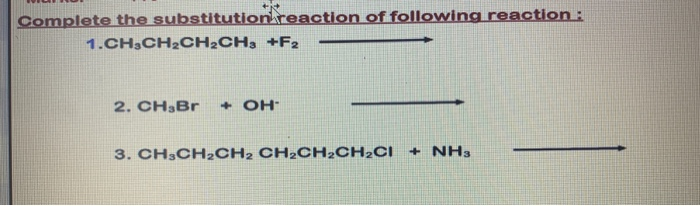
Solved 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Chegg Com

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Equation Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text

Solved Xex Dx 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Chegg Com
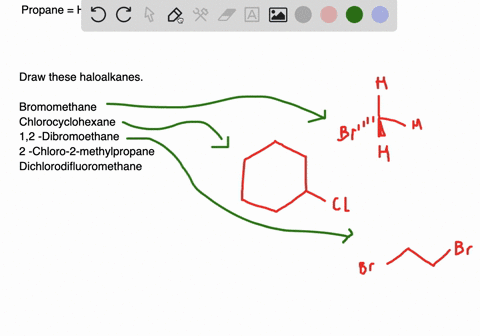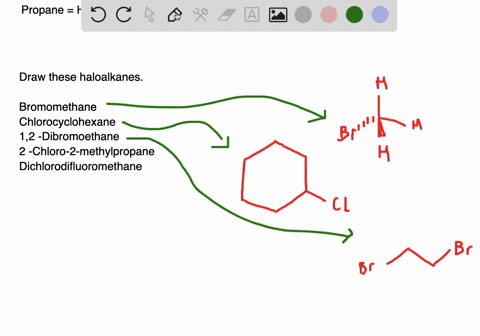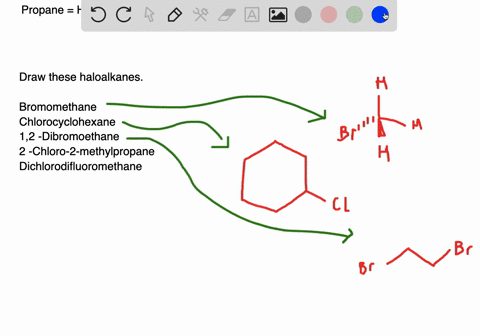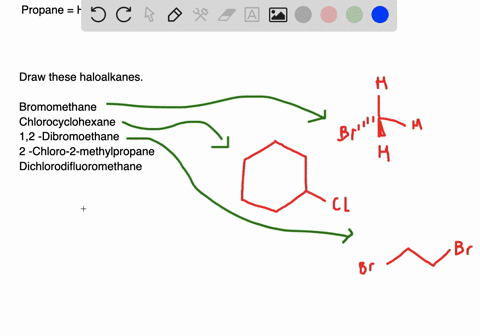
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
0 comments
Post a Comment